Exporting Dried Cocoa: From Farm to Overseas Markets
**Introduction**
Dried cocoa, derived from fermented and dried cacao beans, is a highly sought-after commodity in international markets. Its rich nutrient profile and versatility make it a valuable ingredient in the culinary, health, and cosmetic industries. For exporters, ensuring the highest quality and proper logistics is key to meeting the demands of overseas markets.
**Production and Processing**
1. Cultivation:
– Cocoa beans are sourced from cocoa trees grown in tropical regions. Farmers carefully tend to the trees to ensure healthy growth and optimal bean production.
2. Harvesting:
– Cocoa pods are harvested by hand when they reach full maturity. The beans are then extracted from the pods.
3. Fermentation:
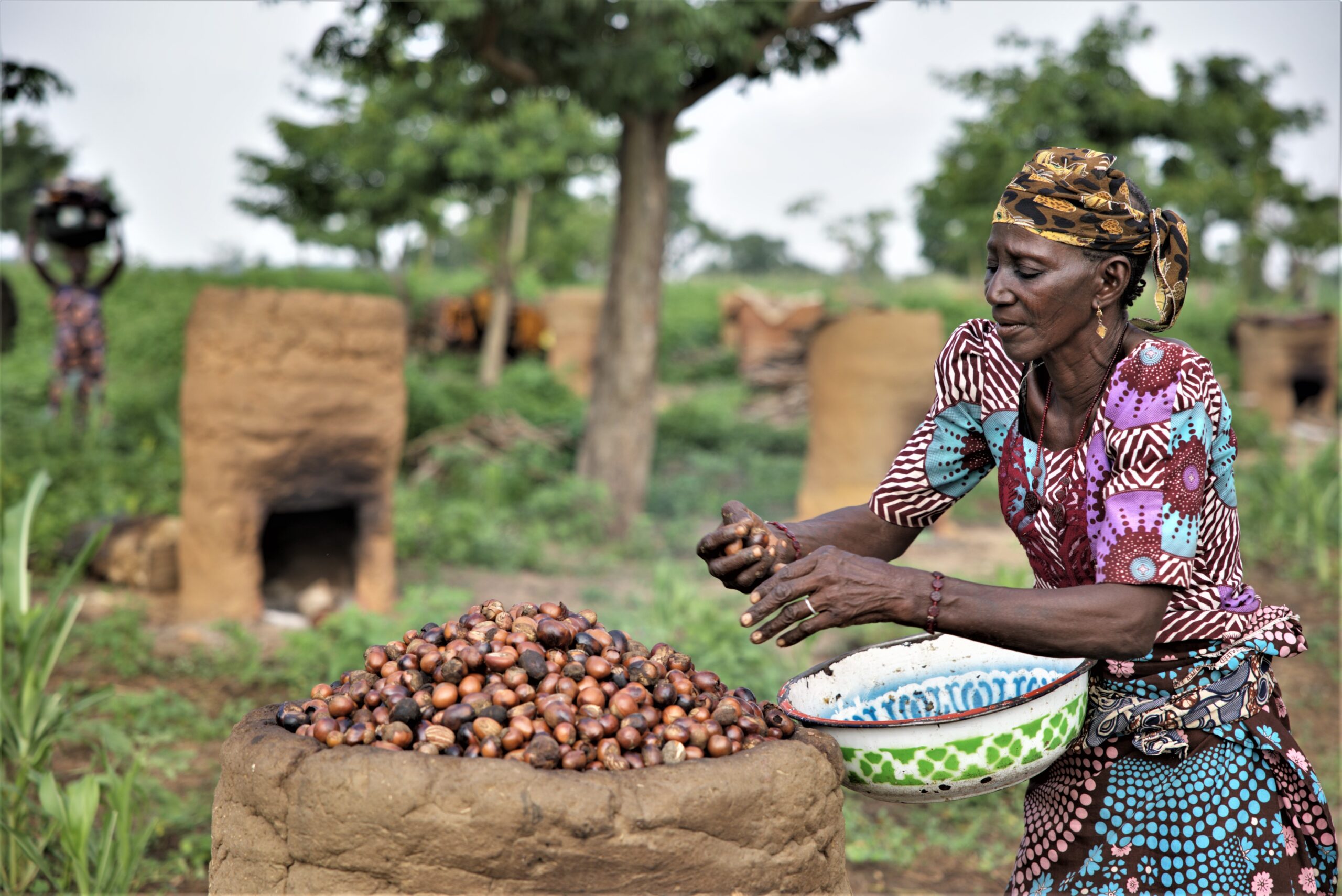
– The beans undergo a fermentation process, which enhances their flavor and reduces bitterness. This process is crucial for developing the rich taste of cocoa.
4. Drying:
– After fermentation, the beans are spread out and sun-dried for several days. This reduces their moisture content and prepares them for storage and export.
Quality Control
1. Grading:
– Dried cocoa beans are sorted and graded based on size, color, and quality. Only the highest quality beans are selected for export.
2. Testing:
– Samples of the dried beans are tested for flavor, aroma, and nutrient content to ensure they meet international standards.
Packaging and Storage
1. Packaging:
– The dried beans are packed in jute or sisal bags, which are breathable and protect the beans during transit.
2. Storage:
– The packed beans are stored in a cool, dry place to maintain their quality until they are ready for shipment.
Logistics and Transportation
1. Shipping Preparation:
– Exporters work with logistics companies to prepare the beans for shipment. This includes obtaining necessary export documentation and complying with international trade regulations.
2. Containerization:
– The packed cocoa beans are loaded into shipping containers, which are sealed and transported to the port.


3. **Overseas Transportation**:
– The containers are shipped via sea freight to international markets. Shipping routes are carefully planned to ensure timely and safe delivery.
**Arrival and Distribution**
1. **Customs Clearance**:
– Upon arrival at the destination port, the shipment undergoes customs clearance. All documentation is reviewed, and the beans are inspected by local authorities.
2. **Local Distribution**:
– Once cleared, the cocoa beans are distributed to local buyers, which may include chocolatiers, food manufacturers, and cosmetic companies.
**Marketing and Sales**
1. **Market Research**:
– Exporters conduct market research to identify potential buyers and understand the preferences of different markets.

2. **Building Relationships**:
– Establishing strong relationships with overseas buyers is crucial. This involves regular communication, providing samples, and ensuring consistent quality.
3. **Branding and Promotion**:
– Effective branding and promotion strategies help exporters differentiate their products and attract new customers.
**Conclusion**
Exporting dried cocoa requires meticulous attention to quality, logistics, and market dynamics. By maintaining high standards throughout the production and transportation process, exporters can successfully deliver premium cocoa beans to overseas markets, satisfying the growing global demand for this versatile and nutritious superfood.